

The body hits the ground at a distance d away from the base of a cliff that has a height of 30 m. Suppose you have a body that rolls off a cliff with a velocity of 5 m/s. There are two components to the initial velocity: horizontal and vertical. Projectile motion without an angle equation examples. Please assume that the initial velocity is u and the projectile angle is 𝛳. vy vyo - gt x horizontal distance (m) y vertical distance (m) v velocity (combined components, m/s) vx horizontal velocity (m/s) vy vertical velocity (m/s) vxo initial horizontal velocity (m/s) vyo initial vertical velocity (m/s) t time (s) g acceleration due to gravity (9. Kinematic Equations for Projectile Motion: Initial Velocity formula: The acceleration pointing down remains constant during the flight of cannonballs. Only the acceleration due to gravity, 9.8 m/ s 2, governs this type of motion. The velocity along the X-axis remains constant throughout the motion, whereas the velocity along the Y-axis varies with its position. As the path of projectile motion is always parabolic, it is represented as:īefore reaching the earth, the cannonball will take a parabolic route during its journey. Any object moving in this manner is referred to as being in projectile motion. It is tracing this curved route known as a trajectory, which has the form of a parabola. From here on out, it will continue to go forward but in a downward direction. It begins to go upward and forward until it reaches its maximum height.
#PROJECTILE MOTION FORMULA HOW TO#
Now let us see how to calculate projectile motion:Īssume you’re shooting a cannonball. In projectile motion, you only need to provide force at the start of the trajectory the object is only affected by gravity after that. As a result, projectile motion is two-dimensional. Substitute t by 2 V0 sin () / g and simplify to obtain the range AC. range AC x V0 cos () t at t time of flight 2 V0 sin () / g. The object, in this case, travels vertically and horizontally at the same time. Horizontal Range of a Projectile (distance AC in the figure above) Distance AC which is the horizontal range is equal to x when t is equal to the time of flight 2 V0 sin () / g obtained above. When an object is launched and moves along a symmetrical parabolic path, the motion is referred to as projectile motion.The object’s parabolic path is referred to as its trajectory. This post will look at the parameters and how to calculate projectile motion in a detailed analysis. When an object is launched, it follows a parabolic path and the motion known as projectile motion. Y = (140)(tan 66.4°) – Īnswer: Vertical height when the ball reaches the end of the field is 24.4 m.

Calculate the vertical height when the ball reaches the end of the field. Solve this by using the trajectory formula. To find the magnitude of the velocity, the x and y components must be added with vector addition: v2 vx2 + vy2. In projectile motion problems, up is defined as the positive direction, so the y component has a magnitude of 49.0 m/s, in the down direction. In the ball's direction of travel, the end of the field is 140.0 m away. Įxample 2: If Trevor hits a ball with his bat at an initial velocity of 45 m/s in the air. Y = x tan 60 - (9.8)(x 2)/(2)(6 2)(cos 2 60)Īnswer: Hence the equation of the trajectory of the projectile is y = x√3 - 0.544x 2.
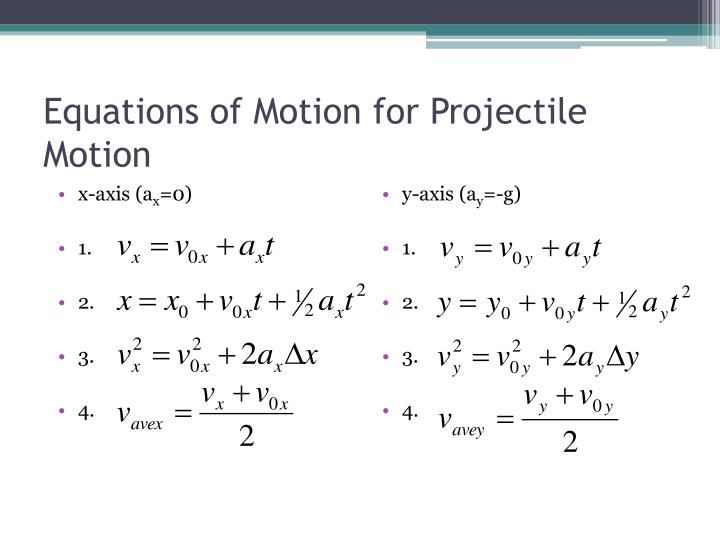
By using this formula, if we know the initial values of the motion, then the exact path of the projectile can be well predicted even without seeing the actual path of the projectile. Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected near Earths surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are passive and assumed to be negligible). What is the Trajectory Formula?Ī trajectory formula is used to tell the path of the projectile. Let us understand the trajectory formula using solved examples. When a stone is thrown in the air, then the parabola is the correct approximation of the path of the projectile. The term trajectory is used for projectiles or heavenly objects. The trajectory formula is used to find the trajectory or the flight path of a moving object which is moving under the action of gravity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
